Inside Plug’s Hydrogen Production Process: Key Components and Project Lifecycle
Hydrogen is emerging as a key energy source in the shift towards a greener future. It offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, helping reduce carbon emissions and support cleaner technologies. Hydrogen production plants play a vital role in producing and distributing this energy on a large scale.
Plug stands out as a leader in the hydrogen economy, working tirelessly to enhance the technology and infrastructure behind hydrogen production. With a focus on clean energy solutions, Plug’s advanced systems ensure efficient production, storage, and transport of hydrogen. In this blog, we will explore the main components of a hydrogen production plant like Plug’s first ever green hydrogen production plant in Camden County, GA USA and highlight how Plug is paving the way in this field.

Let’s dive into the step-by-step process that turns water into hydrogen and see how Plug contributes at every stage.
Hydrogen Production Workflow Overview
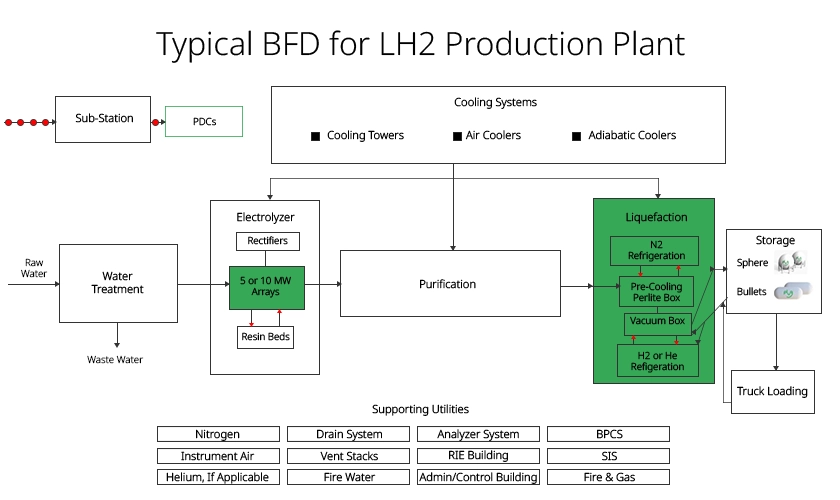
Producing hydrogen on an industrial scale involves several crucial steps, each ensuring high-quality hydrogen that can be used for storage, transportation, or power generation. Below is a detailed breakdown of each stage, reflecting the process depicted in the Typical Hydrogen Production BFD diagram.
1. Water Treatment and Purification
- Why It’s Important: Water must be highly purified before it is fed into electrolyzers to ensure the electrolysis process runs efficiently. Even minor impurities can hinder the efficiency and longevity of the electrolyzer stacks.
- The Process: Raw water is treated to remove total dissolved solids (TDS), organic compounds, and hardness. The goal is to reach the purity and resistivity levels that are required by electrolyzer stacks.
- Plug’s Role: Plug uses advanced Multi pass Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology to maintain water purity, ensuring minimal waste while conserving water resources during treatment.
2. Electrolysis Process
- How It Works: Electrolyzers split purified water into hydrogen and oxygen using electrical energy. This is a zero-emission process, making it a cornerstone of green hydrogen production.
- Technology at Play: Plug deploys proton exchange membrane-based electrolyzers that offer high efficiency and scalability. The electrolyzer systems are designed to integrate with renewable energy sources like solar or wind to further enhance sustainability.
- Plug’s Innovation: Plug’s electrolyzers operate using 5-10 MW arrays to scale to the size plant needed, reducing energy losses, and optimizing hydrogen output to meet growing market demand.
3. Liquefaction Systems
- Why It’s Important: Hydrogen must be cooled and liquefied to make it easier to store and transport. The liquefaction process condenses gaseous hydrogen into liquid form by lowering the temperature to -253°C.
- How It Works: Liquefaction technology includes a pre-cooling section which happens inside a perlite cold box and by utilizing either liquid or cryogenic gaseous nitrogen refrigerant and a liquefaction section which happens inside a vacuum cold box by utilizing hydrogen or helium refrigerant.
- Efficiency Focus: Plug’s cooling systems ensure minimal energy waste during liquefaction, improving the overall efficiency of hydrogen production plants.
4. Storage and Transportation
- Storage Options: Once liquefied, hydrogen is stored in spherical tanks or bullet-shaped containers designed for safety and long-term storage. Plug ensures these storage systems meet the highest safety standards.
- Transport: Hydrogen is loaded into specialized cryogenic trucks and distributed to industries and fueling stations. These distribution networks are critical for expanding the hydrogen economy.
- Plug’s Expertise: Plug offers tailored storage and transportation solutions, ensuring hydrogen is safely delivered to meet global demand.
5. Supporting Systems and Safety Protocols
- Utilities: In addition to the core production process, hydrogen plants rely on systems like nitrogen and instrument air to maintain safe operations.
- Safety Systems: Hydrogen plants must manage fire risks effectively. Plug’s plants are equipped with vent stacks, drainage systems, and real-time gas analyzers to prevent emergencies.
- Continuous Monitoring: Advanced control systems monitor gas composition and ensure operational safety, with a focus on minimizing risks at every stage.
Project Lifecycle: Plug’s Approach to Hydrogen Projects
The success of any hydrogen production plant depends on a well-structured project lifecycle. From planning and design to execution and startup, Plug follows a comprehensive project management strategy to ensure each plant is delivered efficiently on time, and within budget. This approach involves multiple phases, each contributing to the seamless delivery of hydrogen projects.
1. Prospecting and Qualification
- What Happens in This Phase: This phase focuses on evaluating the feasibility of new sites for hydrogen production. Key factors include environmental regulations, infrastructure needs, and land availability.
- Plug’s Approach: The company identifies regulatory requirements early, engages environmental consultants, and analyzes site-specific risks.
- Deliverables: Land lease agreements, initial funding requests, and a high-level business case are developed during this phase to guide decision-making.
2. Define and Design (FEED/FEL)
- What It Entails: The Front-End Engineering Design (FEED) phase defines the scope and technical requirements for the project. Long-lead equipment orders and design documents are finalized during this phase.
- How Plug Manages Design: Plug creates a detailed risk plan, files environmental permits, and establishes contracting strategies, ensuring smooth progress through the design phase.
- Milestones: Final scope of work is established, risk assessments are completed, and the construction management plan is put in place.
3. Procurement and Construction
- Activities in This Phase: Construction includes site preparation, civil and electrical work, and mechanical installations. Key materials and equipment are procured from vendors, ensuring that timelines are met.
- EPC Strategy: Plug follows an Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) strategy to minimize risks and streamline project delivery. This means they take full responsibility for the plant’s design, procurement, and construction.
- How Plug Ensures Quality: Vendors and contractors are evaluated based on their safety standards, workload capacity, experience, and financial stability. Inspections and audits are conducted throughout the process to maintain quality control.
4. Commissioning and Startup
- Commissioning Process: During this phase, all plant systems are tested and verified to ensure proper functioning. Plug conducts detailed system checks, including fire and gas safety tests, before going live.
- Startup Planning: Plug develops a detailed startup plan that outlines key tasks, responsibilities, and contingency measures for handling unforeseen challenges during the startup phase.
- Final Checks: A Pre-Startup Safety Review (PSSR) ensures that all systems are safe and compliant before full-scale operations begin. This is followed by a post-startup review to gather lessons for future projects.
5. Risk Management and Continuous Improvement
- How Plug Manages Risks: Risk assessment is continuous throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring that potential issues are addressed proactively.
- Continuous Learning: Plug documents lessons learned from each project to improve future designs and processes. Their risk management strategy involves regular audits and feedback loops, ensuring projects are delivered smoothly.
6. Supporting Systems and Utilities in Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen production plants rely not only on core components like electrolyzers and compressors but also on essential utilities and safety systems. These supporting elements ensure that the plant operates smoothly, efficiently, and safely.
Nitrogen Systems
- Nitrogen is used as a pre-cooling stage in liquefaction. In addition, nitrogen is used to maintain inert environments, minimizing the risks of fire and contamination in sensitive areas.
- Plug incorporates advanced nitrogen systems to ensure operational safety and reduce hazards.
Instrument Air Systems
- Instrument air is vital for controlling valves and instruments used throughout the plant.
- Plug integrates high-quality air systems to ensure smooth and precise operations across the plant’s infrastructure.
Fire Safety Systems and Emergency Management
- Fire protection is essential when working with hydrogen, which is highly flammable.
- Plug ensures fire safety with specialized vent stacks, drainage systems, and fire water supplies. Advanced gas detection systems monitor for potential leaks and other hazards.
Waste Management Systems
- Efficient handling of waste products like excess hydrogen or water ensures the plant meets environmental standards.
- Plug adopts sustainable waste management practices to minimize the environmental impact.
Cooling Systems
- Various cooling technologies such as cooling towers, air coolers, and adiabatic coolers maintain optimal operating temperatures based on location and environmental conditions.
- Plug’s cooling solutions ensure energy-efficient operations, reducing the overall carbon footprint of the plant.
Analyzer and Monitoring Systems
- Real-time monitoring systems analyze gas composition and ensure compliance with quality and safety standards.
- Plug’s monitoring technology provides continuous feedback to keep operations running smoothly and safely.
Conclusion
Hydrogen production is at the heart of the clean energy revolution, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. A hydrogen production plant is a complex system that requires precise planning, advanced technologies, and seamless coordination. Plug has positioned itself as a leader in this space, driving innovation and efficiency at every stage.
From water treatment to electrolyzer and liquefaction technologies, Plug’s solutions are designed to meet the growing demand for hydrogen with sustainability in mind. The company’s structured project lifecycle ensures that each plant operates with the highest standards of safety, efficiency, and environmental compliance.
Through continuous improvement, risk management, and a focus on innovation, Plug is not just producing hydrogen but paving the way for a greener future. With a commitment to scaling clean energy solutions, Plug is helping industries and communities transition toward sustainable energy sources.
As hydrogen becomes more critical in the global energy landscape, Plug’s contributions are setting the benchmark for excellence. Our efforts show that the future of energy is not just about production, it’s about doing it right.
References:
- https://www.plugpower.com/water-electrolysis-powering-the-world-with-green-hydrogen/
- https://www.plugpower.com/hydrogen-electrolyzers-101-why-they-matter-for-sustainable-energy/
- https://www.plugpower.com/hydrogen-electrolyzers-five-frequently-asked-questions/
- https://www.plugpower.com/blog/green-hydrogen-101-unlocking-the-potential/